Fats are often misunderstood and have long been demonized in diet culture. Lots of misconceptions have built around these important macronutrients that actually play a crucial role in our body’s optimal functioning.
In this article, we’ll look into the different types of fats, separating the good from the bad, and learning how incorporating the right fats into your food choices can enhance your overall health and well-being.
Table of Contents
What are Fats?
Fats are also known as lipids or fatty acids that are made up of a three-molecule structure called “triglyceride”. Fats play multiple roles in the proper functioning of our body. They serve as a vital component of a balanced diet which provides us energy, warmth, and protect our skeleton and nerves.
Most of the fat that we need is made by our body, however there are some types of fats, like Omega-3 and Omega-6, which our body cannot produce, hence we need to obtain them from the foods we consume. These fats are known as “essential fats”.
Fats are a concentrated source of energy that provides more than twice the amount of energy (9 calories per gram) compared to carbohydrates and proteins (4 calories per gram).
Types of Food Fats
There are mainly three types of fats that we obtain from our food.
- Saturated fats
- Unsaturated fats
- Trans fats
Understanding the diverse types of fats is crucial, as different fats influence our heart-health differently.
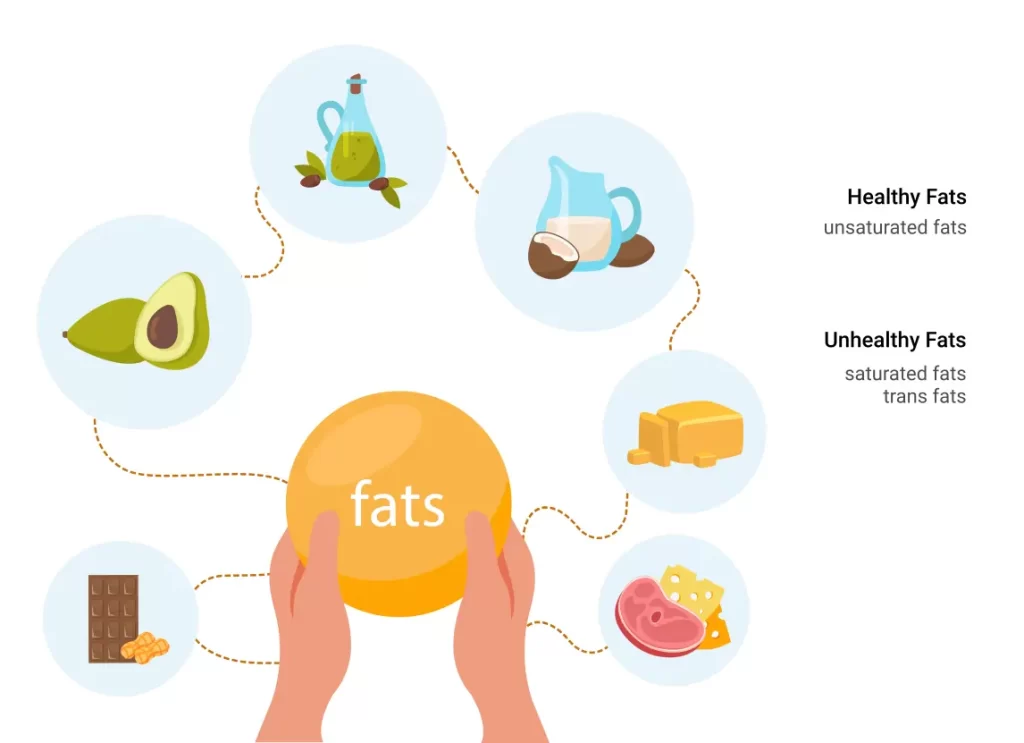
Saturated Fats: (Unhealthy Fats)
Saturated fats are predominantly found in animal products, tropical oils, and processed foods. They can contribute to elevated levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) which increases cardiac risks when consumed excessively. These fats remain solid at room temperature, hence often referred to as solid fats.
UK health guidelines recommend that an average man should eat no more than 30g of saturated fat a day and an average woman should consume less than 20g; while as per the American Heart Association (AHA), people should not consume more than 13g of saturated fats per day.
Foods that contain saturated fats
Saturated fats are commonly found in below listed food products.
| Animal based | Cream, Butter, Cheese, Ice cream |
| Plant based | Coconut, Palm oil, Palm kernel oil, Cocoa butter |
| Meat based | Beef, Lamb, Pork, Poultry, Tallow, Lard |
| Processed food | French fries, Packaged snacks, Fried snacks, Pastries |
Unsaturated Fats: (Healthy Fats)
Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered heart-healthy and can be found in plant-based oils, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. Consuming these sources of healthy fats can help lower bad cholesterol levels in your blood, which in turn reduces the risk of heart disease.
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet offers a plethora of benefits for overall health and well-being. They play a crucial role in reducing inflammation, depression, and anxiety. It also promotes brain function by improving cognitive abilities.
Foods that contain unsaturated fats
- Nuts and seeds: walnuts, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, almonds, hazelnuts, pecans, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds
- Vegetable oil: olive, canola, corn, soybean, sunflower, peanut, sesame
- Fish: anchovies, herring, mackerel, black cod, salmon, sardines, bluefin tuna, whitefish, striped bass and cobia
- Other foods: avocado, peanut butter, tofu, soybean
Trans Fats: (Unhealthy Fats)
There are two broad categories of trans fats found in our food: naturally-occurring and artificial trans fats.
Naturally-occurring trans fats are produced in the digestive system (gut) of certain animals and the food derived from these animals, such as dairy and meat products, may contain small amounts of these fats.
Artificial trans fats, on the other hand, are primarily produced through industrial processes that involve hydrogenation of liquid vegetable oils to solidify them. These trans fats are popularly known as “partially hydrogenated oils” in the processed food industry and are universally recognized as detrimental to health due to their association with increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Despite their adverse health effects, trans fats remain popular among companies due to their convenience, low production costs, and extended shelf life. They impart a desirable taste and texture to foods. Numerous restaurants and fast-food establishments opt for trans fats in their deep-frying processes, as oils containing trans fats can be reused multiple times in commercial fryers.
Smart Food Choices
When it comes to snacking, making informed choices about the types of fats you consume can significantly impact your health. Opting for foods that are rich in healthy fats can provide sustained energy, promote satiety, and contribute to overall well-being.
Choose nuts, seeds, avocados, olives, Greek yogurt, and other foods that contain healthy fats. These foods not only provide a satisfying crunch or creaminess but also deliver essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Whether you’re making homemade granola bars, trail mix, or vegetable dips, these ingredients add texture, flavor, and nutritional value to your foods.
When it comes to cooking and preparing foods, it’s important to pick methods that preserve the nutritional integrity of healthy fats. Opt for cooking techniques like baking, grilling, steaming, or sautéing with minimal oil to avoid unnecessary calories and reduce the risk of oxidizing healthy fats.
Additionally, be mindful of portion sizes to ensure you’re enjoying these fat-rich foods in moderation. By selecting foods that prioritize healthy fats, you can nourish your body and satisfy your cravings without compromising your health goals.
Conclusion
Fats play a vital role in our diets, offering both essential nutrients and concentrated energy. By understanding the differences between healthy and unhealthy fats, we can make informed choices that promote our overall well-being. As we navigate our snack choices, let’s prioritize options rich in unsaturated fats, such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.
Remember to enjoy these foods in moderation, and embrace cooking methods that preserve the nutritional integrity of healthy fats. By adopting these practices, we can cultivate a balanced approach to snacking that nourishes our bodies and enhances our quality of life.