The modern world is increasingly acknowledging the prevalence of lifestyle diseases and global issues such as climate change and food security.
Millets, often hailed as superfoods, not only provide substantial health benefits but also offer significant socio-economic advantages.
This article addresses common questions about millets, such as their varieties, health advantages, and more. Let’s explore how millets could revolutionize our approach to farming and dietary habits. For easy access, feel free to use the table of contents to jump to the particular topic that you’re interested in, or watch an informative video highlighting the significance of millets.
Table of Contents
What are Millets?
Millet is a collective term used for a group of small-seeded, thick, and coarse grains that have been cultivated for thousands of years, primarily for human consumption and animal feed.
These grains belong to the botanical family of Poaceae (cereal grass) and are widely grown in arid, semi-arid and tropical regions around the world. It also grows well in mountainous, tribal, and rain-fed regions.
Types of Millets
There are different types of millets available in India which are region specific with its own unique profiles and benefits. Here you can find a comprehensive list of millets commonly available in India with their colloquial names.
Major Millets
| English Name | Regional Indian Names |
|---|---|
| Pearl Millet | Bajra | Bajri |
| Sorghum | Jowar | Juar | Jowari |
| Finger Millet | Ragi | Bavto | Nagli | Mandhal |
Minor / Small Millets
| English Name | Regional Indian Names |
|---|---|
| Foxtail Millet | Kangni | Kang |
| Proso Millet | Barri | Cheena | Varigulu | Cheno |
| Barnyard Millet | Jhangora | Sanwa | Samo | Swank |
| Little Millet | Kutki | Kuri |
| Kodo Millet | Kodra | Harka |
| Brown top Millet | Hari Kang | Makra | Korale |
Pseudo Millets
| English Name | Regional Indian Names |
|---|---|
| Amaranth | Rajgira | Hena | Bari | Chaulai | Ramdana | Cheno |
| Buckwheat | Kuttu |
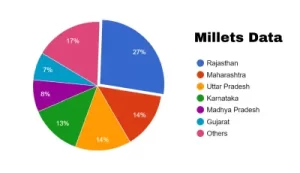
Bajra, Jowar and Ragi are the most growing varieties in India. They contribute about 60%, 25% and 10% respectively, of total millet production in India. Millets are grown across India. Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat are the major producing states.
As the name suggests, Pseudo millets are not the millets in its true sense nor do they belong to the same botnical family (Poaceae) as other millets do. However, they are nutritionally same and consumed in the similar ways as other cereal grains do, hence called the Pseudo millets / grains.
Nutrient Contents of Millets
Millets are renowned for their nutritional density. Their rich nutrients like essential vitamins, carbohydrates, protein, dietary fiber, substantially high amounts of minerals, and antioxidants contribute to overall health and well-being.
Important nutrient contents
- Rich in Essential Vitamins: Vitamin A, C, and B-complex
- High in Minerals: Magnesium, Manganese, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Iron, Zinc, Calcium, and Copper
- High Dietary Fibers and Bioactive Substances: Resistant starch, Oligosaccharides, Lipids, Flavonoids, and Phenolic acids
Health Benefits of Millets
Gluten-free
Since millet doesn’t contain gluten, it’s a safe alternative for individuals with celiac disease, a chronic digestive and immune disorder triggered by gluten consumption. When gluten intolerant people consume wheat, rice or rye they feel the pain relating to stomach discomfort, bloating, diarrhea, fatigue, and anemia. Millet is the best alternative to regular dietary staple grains for those who need to avoid gluten due to medical reasons.
Low Glycemic Index (GI)
Foods with a low glycemic index release glucose into the bloodstream slowly and steadily, preventing sudden spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. Millet’s low GI means it doesn’t cause rapid increases in blood sugar after consumption. For individuals with diabetes, incorporating low-GI foods like millet into their diet can aid in blood sugar control. Better insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles also help lower the risk of heart disease.
Low in Calories
Millets are low in calories, hence preferred in weight loss or weight maintenance diets. Foods that are lower in calories can help create a calorie deficit, which is necessary for losing weight. Despite being low in calories, millet is rich in fiber and nutrients. This combination promotes feelings of fullness and satisfaction, which can help prevent overeating and snacking between meals.
Contains Good Fats
It supports cardiovascular health by promoting healthy blood lipid profiles, improving blood vessel function, and reducing inflammation in the body. Good fats are essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, which are important for various bodily functions including immune function, bone health, and vision. Since Millets contain good fats, it actually helps in weight management by keeping you feeling satiated and prevents overeating.
Good Source of Protein
Millet provides a source of high-quality plant-based protein that supports muscle maintenance and repair. Protein also plays a role in the absorption of essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, ensuring that the body can efficiently utilize the nutrients from the foods we eat.
No Allergens
For people with allergies to wheat or other grains containing gluten, consuming millet eliminates the risk of allergic reactions such as skin rashes, digestive issues, respiratory problems, or anaphylaxis. Avoiding allergens can help improve respiratory health. Millet’s allergen-free nature expands the range of food options available to those with allergies or sensitivities, allowing them to enjoy a diverse and nutritious diet without compromising their health or dietary restrictions.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants support the immune system by neutralizing free radicals and reducing inflammation. This helps the body fight off infections and diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. It also helps slow down the aging process, keeping skin healthy and youthful. High dietary fiber contents coupled with these antioxidants improve overall health by promoting the elimination of waste products to detoxify your body.
Millets for Sustainable Agriculture & Food Security
Millet holds a rich historical significance in agriculture, serving as a staple crop in many ancient civilizations due to its resilience and adaptability to diverse climates and a wide range of ecological conditions. It is often grown on skeletal soils that are less than 15 cm deep, as it doesn’t demand rich soils for their survival and growth.
Its ability to thrive in arid conditions with extreme climate and degraded soil makes it a vital resource for regions facing environmental challenges and water scarcity. In comparison to most fine cereals such as wheat, maize, or rice, they have minimal obligation of water, fertilizers, and pesticides; hence economical too. Undoubtedly, millets play a vital role in global food security and sustainable agriculture with reduced carbon footprints.
In India, about 25 million small farmers are directly involved in millets production. These are mostly the marginal farmers who have scarce resources. Millet being the economical crop, help these small farmers in fighting poverty. Being a highly drought resistant crop, millets act as a cushion against weather related uncertainties.
The significance of millets in our life, environment, farmers’ income, and national food security is nicely explained in this short video. We recommend watching it till the end.
Production & Consumption of Millets in India
India is the biggest producer and consumer of Millets in the world. It produces around 17-18 Mn MT of Millets per year, which is 19% of the global millet production, and almost the same is the domestic consumption. Millet is grown in 12-13 different states in the country.
Millets have always been a part of India’s staple diet; however, the crop pattern and dietary habits changed post the severe famine of the mid-1960s. This posed a big challenge of food shortage to the growing population of the country. India found its solution in the Green Revolution by promoting high-yielding, genetically-modified varieties of wheat and rice that could fill the empty stomachs.
The Green revolution made India self-reliant in food grain production that ensured national food security. However, it resulted in gradual fall in the production and consumption of millets as more and more farms were shifted towards high yielding wheat and rice crops. Trends of following the fency western foods which are mostly wheat or rice based also resulted in the decline of millets’ demand.
India’s per capita annual millet consumption is about 4 kg in 2022 which used to be around 31 kg in the 1960s. At present, the government of India is putting its efforts to give this nutri-crop its due credit by formulating necessary policies and promoting awareness about its health benefits. This seems to be yielding positive results too.
Our article on millets data will provide you a very insightful knowledge about the millets production and its export from India.
India’s Efforts in Popularizing Millets
Millet is being promoted as a superfood for its nutritional values. India’s Union Finance Minister Shri Nirmala Sitharaman mentioned millets as “Shree Anna” (श्री अन्न) in her 2023 budget speech, saying India is the global hub for millets and is at the forefront of popularizing them.
Addressing a public rally, India’s Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi revealed that the name Shree Anna (Mother of all grains) is picked from the colloquial word for Millet in Kannada language. It is derived from the original word ‘Siri Dhaanya’, meaning the grains that bring prosperity and wealth.
India observed 2018 as the National Year of Millets to boost production and awareness of millets. United Nations also declared year 2023 as the International Year of Millets on India’s proposal.
Shri Modi inaugurated the Global Millets (Shree Anna) Conference in March-2023 in New Delhi, India. In the two-day global conference, the important issues relating to Millets like promotion and awareness of its benefits amongst producers, consumers and other stakeholders were discussed.
India’s campaign is a significant step in the direction of food security and responsible agriculture. It will help in improved acreage of this super crop and promote consumption of nutrient rich grains as a staple food. This will substantially contribute to the global fight against hunger and mitigate the effect of climate change in the long run.
Conclusion
Millets have emerged as a nutritional powerhouses, offering a multitude of health benefits while also contributing to sustainable agriculture and global food security. With its rich history, diverse culinary applications, and significant cultural importance, millets stand as a symbol of resilience and versatility in the quest for healthier and more sustainable food choices.
As we continue to explore the potential of millets in modern diets and agricultural practices, let us embrace their bounty and advocate for their widespread adoption, paving the way towards a healthier, more nourished, and environmentally sustainable future.